
About HAE
What is hereditary angioedema (HAE) and how is it treated?
HAE is a rare genetic condition that causes repeat episodes of severe swelling in the body, especially the face, arms, legs, airway, and intestinal tract.
Everyone living with HAE experiences their disease differently, but regardless of where you are in your journey, HAE likely affects—or has affected—your life in a number of ways.

— Leah, living with HAE
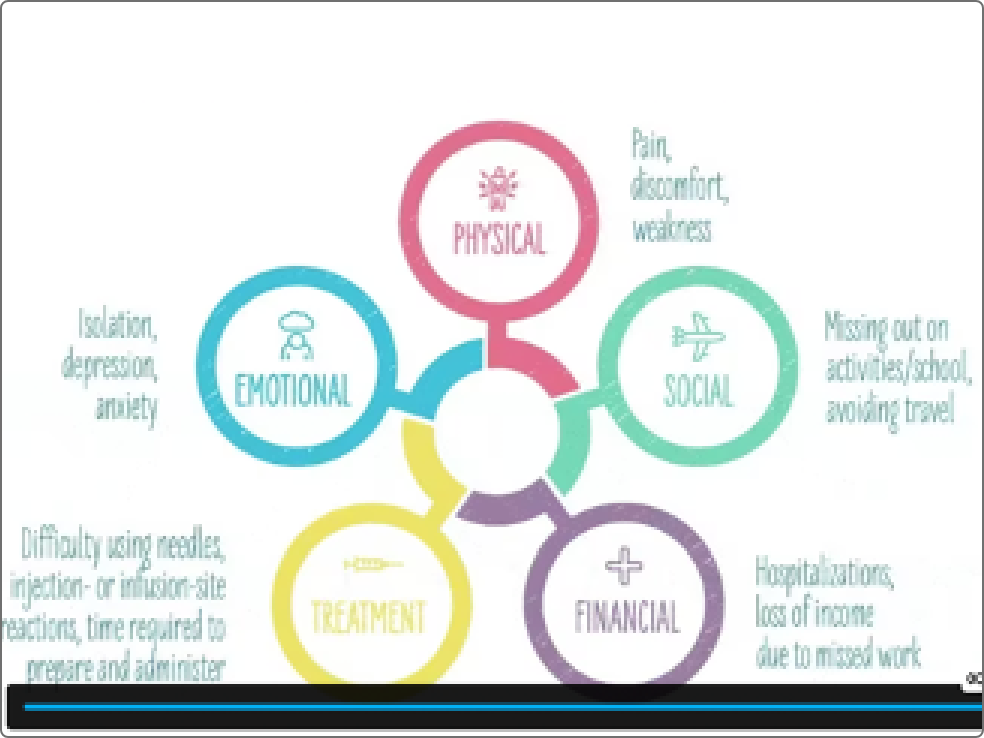
Treating your HAE
There are 2 types of therapies used to treat HAE.
Rescue therapy
Preventative therapy
Because treatment with rescue therapy alone is not always enough, people living with HAE often use both types of therapy to manage their disease. Long-term treatment with preventative therapy is the best way to prevent future HAE attacks.
As your life changes, your treatment plan might need to change, too
Making decisions with your healthcare team can lead to better results. As you and your healthcare provider discuss the preventative therapy that‘s right for you, here are some factors to consider:

— Daryl, father and caregiver to Le‘ah, a patient
Don‘t be afraid to advocate for yourself to get what you want out of HAE management
Every person‘s experience with HAE is unique. But there‘s no one who understands your experience and what you want better than you.
It‘s important to discuss your unique needs and goals with your healthcare provider, because they‘re what make you, you:

Whether or not you‘re the first in your family with HAE

Age

Activity level

Daily and long-term goals

Personal preferences

C1 esterase inhibitor level

— Le‘ah, living with HAE
Learn more about why ORLADEYO could be right for you
Ready to start the conversation about ORLADEYO at your next appointment?
Download the discussion guide and use it to talk to your healthcare provider about your satisfaction with your current treatment and if ORLADEYO could be right for you.